Ultra-Pure Water Analyzer Detects Trace Sodium Levels
Ultra-Pure Water Analyzer Detects Trace Sodium Levels – Precision PPB Level NA Monitoring for Use in Pharmaceuticals, Food/Beverage, H2 Electrolysis, Steam Turbine and Boiler Water, Electronics, Refineries & More
 Anaheim, CA—January 25, 2022—Process and plant engineers requiring ultra-pure or high purity water for a wide range of ingredient and rinsing or washing or feed water applications ranging from pharmaceuticals to food/beverage to green hydrogen (H2) electric power will find the NA6 Sodium Analyzer from Electro Chemical Devices (ECD) sets the standard in providing accurate measurement, reliability and ease of use.
Anaheim, CA—January 25, 2022—Process and plant engineers requiring ultra-pure or high purity water for a wide range of ingredient and rinsing or washing or feed water applications ranging from pharmaceuticals to food/beverage to green hydrogen (H2) electric power will find the NA6 Sodium Analyzer from Electro Chemical Devices (ECD) sets the standard in providing accurate measurement, reliability and ease of use.
Many consumer products and industrial processes rely on ultra-pure or high-purity water. They include pharmaceutical water for injection (WIF), beer or other beverages and food products where water quality affects taste, as well as the sanitary rinsing of clean-in-place (CIP) equipment. Other industrial applications include H2 electrolysis production for green electric power, corrosion prevention in steam turbines for conventional electric power generation, steam boilers in refineries, as well as semiconductor fabrication, glass production and metal plating.
With an advanced glass electrode sensor that measures sodium in water to the parts per billion (ppb), parts per million (ppm) or milligram per liter (mg/l) levels, the ECD NA6 Sodium Analyzer is the flexible water quality assurance tool. The sodium sensor’s measurement range of 0.1 to 10 ppb is based on the proven accuracy of ECD’s sodium glass electrode sensor for the online potentiometric detection of low ppb traces of sodium.
When exposed to raw process or treated process water, ECD’s sodium glass electrode sensor produces an electronic signal potential proportional to the log of the sodium concentration. The sample is exposed to a reagent vapor, which raises the sample pH to 11 to eliminate any pH or ammonium interferences that would affect measurement accuracy. Highly reliable too, reproducibility is ±0.2 ppb or 5%, whichever is greater at constant temperature.
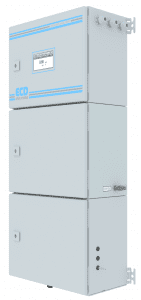
The NA6 Analyzer features a tri-compartment design for reliability and safety. The electronics and user interface display are in the top compartment, with the calibration solutions for autocal in the middle compartment and the wet sample housed in the bottom of the unit. The electronics are always dry and safe from moisture for superior reliability.
NA6 Sodium Analyzer Page 2 of 2
The NA6 features a dual-function design for maximum user flexibility by plant technicians. It features a T90 180 sec (0 to 10 ppb) delay time when in continuous operation. The water analyzer’s “grab sample” capability also enables the unattended analysis of manually collected samples. The results of external samples are stored in the analyzer’s data logger, which includes time and date stamping information for history logging.
For easy installation, the ECD NA6 Analyzer is ready to go right out of the box. It takes a single technician less than 30 minutes with no special training or tools to get the NA6 up and running. All that needs to be done is connect the power, the sample line and the reagent lines. The analyzer is then fully operational.
The NA6 analyzer offers a choice of a manual 1-2 point calibration mode or a 2-point automatic calibration mode. The 2-point automated calibration mode minimizes operator intervention and ensures accurate results are obtained. Free selectable calibration intervals are available too. The results of the last ten calibrations are stored in the analyzer’s internal data logger.
With its built-in color touchscreen user interface with multi-lingual capability, the NA6 Analyzer is highly intuitive. It displays measured values and status information in a large easy-to-read format. The design provides full access to menus and functions. The built-in data logger comes with USB download capability.
Two 4-20 mA data outputs are provided with the NA6 Analyzer, which are compatible with Modbus RTU485 plant control system communications. Three onboard SPDT relays are programmable to set alarms. The standard power supply is 120/240 VAC, 50/.60 Hz, with an available 24 VDC optional configuration.
The rugged, long-life NA6 Analyzer operates over a wide temperature range from 41 – 122 °F (5 to 50 °C). Ingress protection is IP54 compliant. For outdoor use, an optional cabinet enclosure is available for harsh weather conditions.


 Electro-Chemical Devices (ECD) has introduced its new self-cleaning oil-in-water sensor – OIW80 which helps municipal water and wastewater facilities as well as industrial plants to quickly and accurately detect oil in water leak incidents. This technology helps one to take quick action in order to prevent contamination of drinking water, fouling of batch processes, damage to plant equipment or contamination of sensitive water ecosystems.
Electro-Chemical Devices (ECD) has introduced its new self-cleaning oil-in-water sensor – OIW80 which helps municipal water and wastewater facilities as well as industrial plants to quickly and accurately detect oil in water leak incidents. This technology helps one to take quick action in order to prevent contamination of drinking water, fouling of batch processes, damage to plant equipment or contamination of sensitive water ecosystems. The new OIW80 Sensor from Electro-Chemical Devices (ECD) has given a boost to engineers at municipal water or wastewater facilities and industrial plants.
The new OIW80 Sensor from Electro-Chemical Devices (ECD) has given a boost to engineers at municipal water or wastewater facilities and industrial plants.
